6 keys to choose a binocular
Everything you need to know to choose your binocular or binocular
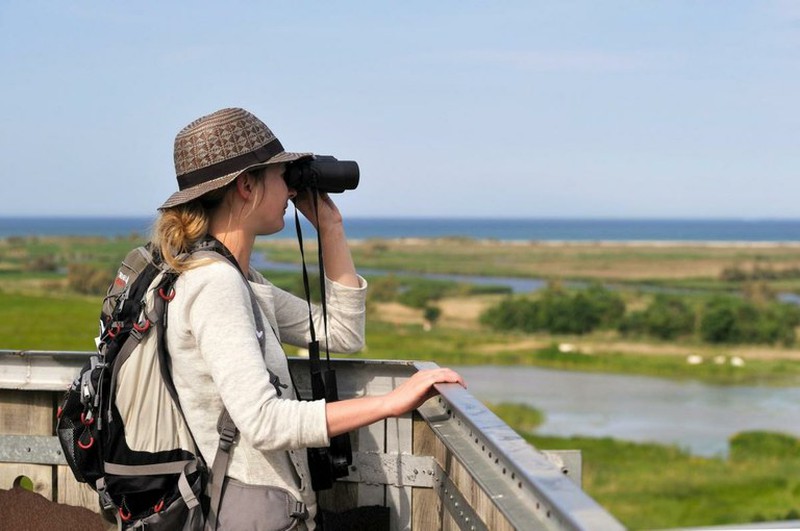

Below we will detail what each of the most common characteristics that we find when looking at the descriptions of the binoculars means:
1) Magnification: The magnification or power is the ability of the binocular to bring us closer to the image that we are observing. If we have a 10X magnification we will see the object 10 times closer. If it is at 100m we will see it as if we had it at 10m (Distance / increase).
2) Aperture: The diameter of the objective lens or aperture determines the entry or capture of light. The more aperture, the more light enters our binocular and the more definition of the object observed. A 50mm lens captures 1.56 times more light than a 40mm lens and 2.78 times more light than a 30mm lens.
3) Field of view: Either in m or in º, is the width (m) of the area visible through the binoculars at a standard distance of 1000m. If we treat it in º we have that the real angular field of view indicates the value of the angle of the visible portion of a circle (360º), but the apparent angular field of view is more useful, which indicates the angle formed between the two ends of vision through the binocular. Apparent angular field of view = actual angular field of view x magnification.
4) Exit pupil: It is the cone-shaped beam of light that comes out of each of the eyepieces. It is obtained by dividing the diameter of the objective by the magnifications. This value coincides with that of the relative luminosity , indicating the amount of light that reaches our eyes. The greater the exit pupil, the greater the luminosity of the binocular. The ideal is between 4 and 6mm.
5) Eye relief: It is the distance that must be between our eyes and the eyepieces so that our pupil diameter equals the diameter of the exit pupil, in this way we get to see our entire visual field illuminated. The greater the distance, the greater the viewing comfort, the ideal moves between 10 and 17mm.
6) Minimum focus distance: It is the minimum distance value at which we can focus on an object. From 8m we consider a good minimum focus distance. The binoculars incorporate a focus adjustment and also a diopter adjustment depending on the observer's vision.
7) Optical structure: In the market we find two different types of structure, the prism binoculars in joint and the prism binoculars in the ceiling. Porro binoculars have the prisms arranged non-linearly, therefore the eyepieces are not aligned with the objectives. Binoculars with ceiling prism feature aligned prisms and a more complex and uniform structure.
8) Optical quality : The optical quality is determined by the quality of the prisms, which can be Bak-7 of boro-silicate glass or Bak-4, of higher optical quality, sharpness, contrast, luminosity and higher index of refraction. Then we find the optical treatment of the lenses, among which we distinguish between multi-coated or "fully multi coated" optics and other optical treatments to highlight, such as the ED treatment (extra-low-dispersion) and the HD treatment or high definition. At the same time, we also highlight fluorite treatments in the most advanced binoculars. These optical treatments attempt to minimize or eliminate chromatic aberrations, optimize contrast, optimize image definition and improve observation in the most difficult environmental conditions, including those with low light.
1- The first dilemma before choosing which binocular we buy, is the use that we are going to give it. In a first step we differentiate between:
a) Earth observation binoculars
Designed for the observation of terrestrial or marine landscape, fauna and flora.
b) Astronomical observation binoculars
Designed for the most visible astronomical, lunar, constellation and planetary observation.
2- Earth observation binoculars are normally intended for wildlife and landscape observation. Interested in a binocular between 8 and 10 magnifications and with an opening of between 32 and 42mm, at higher magnification we would lose stability, field of vision and would necessarily need a tripod. In ornithology, the standard recommendation is 8 / 10x42mm
It should also be borne in mind that the field of vision is reduced at higher magnification, so if we want to have a wider or panoramic view of the environment, we will recommend binoculars of between 7 and 8 magnifications, both in joint prism and in ceiling prism.
3- In places with little light, such as inside the forest or for the observation of large landscapes, we recommend openings of 42 to 56mm in diameter and more specialized optical treatments, such as ED or HD, which make us gain definition in low-light conditions.
Changing environmental and meteorological conditions is also an important "handicap" in the use of binoculars. On the ground and especially in the mountains, the luminosity varies constantly, with reflections, more illuminated areas, foggy conditions, twilight rays, etc. In these conditions and for recurrent use in this environment, we also recommend binoculars that incorporate a higher Optical treatment, ED treatment works very well in these conditions as well as HD treatment helps to gain color definition in low light conditions. Binoculars with lenses made of fluorite offer us the highest quality features, a factor that also makes the difference in wildlife and ontological observation in great detail.
4- The weight of the binocular is also vital according to what uses, for hiking and traveling, handy and lightweight binoculars are recommended, so as not to excessively ballast the luggage. So if our excursions are in the mountains and we have a naturalistic interest, we recommend 8 X 28, 8 X 32 or 10 X 32 models. On the other hand, for travel we can sacrifice a little opening, for a much lighter tool, so we will choose 8 binoculars x 25, 10 x 25 or 8 x 28.
In other uses, such as hunting or observations from a more stable location, then we can use binoculars of greater scope, performance and weight. We will get from 10 to 15 increases and we will jump to openings between 42 and 56mm. They are binoculars with a large field of view and must be used with a tripod.
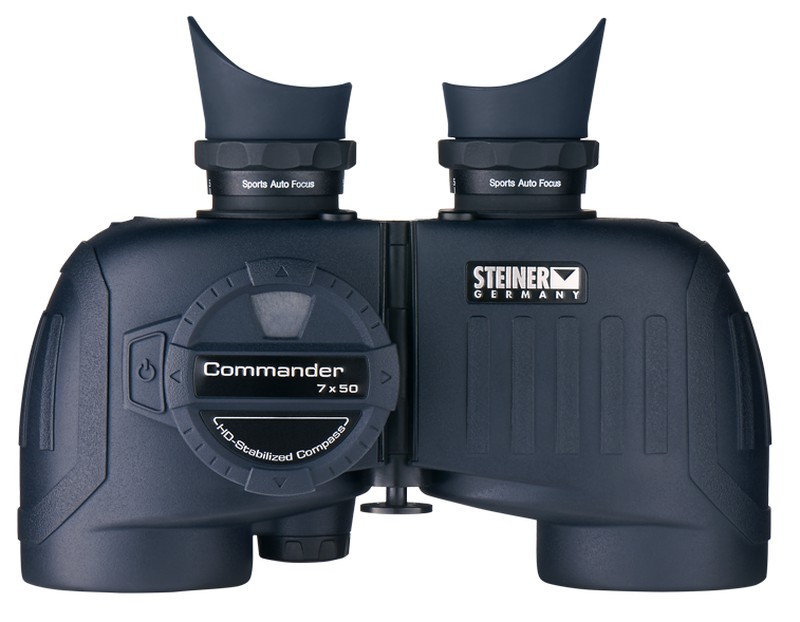
5- If on many occasions it is no longer easy to keep balance inside a boat, imagine yourself with binoculars in hand and wanting to fix your sight on an observation point. To solve this problem, the nautical binoculars are made with low magnification, 7x, and large apertures, between 30 and 50mm. They are very stable binoculars with a wide field of vision, to cover a wide perspective.
The nautical binoculars can come equipped with a compass, which is used for orientation, and with a rangefinder, which is used to calculate how far a certain object is from our position.
Finally, note that the nautical binoculars are water resistant and even some models, submersible up to a few meters.
6- Astronomical binoculars are designed for observing the constellations, the moon and even some of the most visible planets from Earth such as Mars, Jupiter and Saturn. It is a first step to learn to locate the stars and orient ourselves in spatial geography.
For this use we recommend binoculars with high magnification and aperture, normally greater than 12x and with apertures greater than 70mm. We are interested in gaining as much light as possible, taking into account that we observe in dark conditions. At the same time we are interested in a long range, precisely to be able to observe stars and planets that are far away.
With an astronomical binocular we can observe in detail the lunar surface and identify its most important features and craters. With binoculars of higher magnification, greater than 20x, planets such as Jupiter, Mars or Saturn can be identified. It is very common to use astronomical binoculars before or during astronomical observation with a telescope.









Opinions of our clients
Receive our news