What is the wind?
Everything about this meteorological variable and how to measure it

We will start with that phrase that sentenced us at school: "The wind is air in motion . "
Once we have this sentence, we wonder why this movement is generated?
We live under the influence of air masses, these air masses of the troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) are subject to temperature variations and consequently volume and mass variations that end up translating into pressure variations.
Thus, these variations in temperature and pressure produce displacements of air masses and, consequently, wind, moving air. We can conclude "roughly" that the wind is produced by variations in temperature or atmospheric pressure.
A practical example of the wind by variation of Tª are the air currents that are generated inside the house and an example of the wind by variation of atmospheric pressure would be the typical cyclonic wind of a storm.
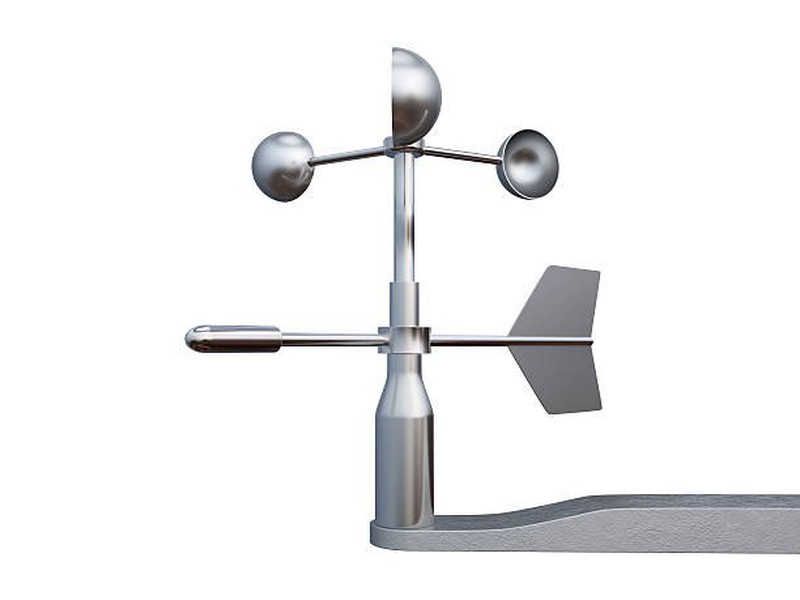
The wind is measured with the anemometer, which is a measuring instrument made up of blades or a windlass, which translates the speed of rotation or revolutions of the blades into wind speed.
This is the basis for all the digital anemometers that we know today, whether they are portable or associated with a complete weather station. Wind measurement units can be in Km / h, m / s, knots, mph, etc ...
A relevant factor is the measurement range of the anemometer, which is particular to each instrument. The maximum streak value will depend on this interval which can range from 0.5 seconds to 5 or 10 seconds. The longer the interval time, the lower the maximum streak speed.
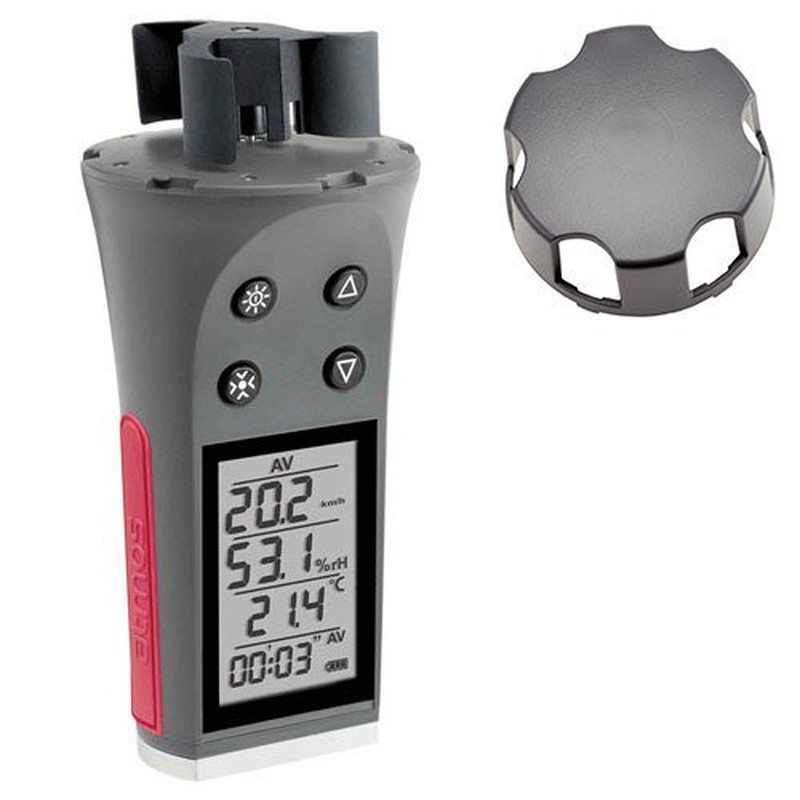
- Portable digital anemometers:
They are instruments for hiking, trekking, mountaineering or nautical activities. They help us control environmental conditions and avoid dangerous situations. These devices can measure wind, temperature, wind direction, humidity, pressure and altitude.
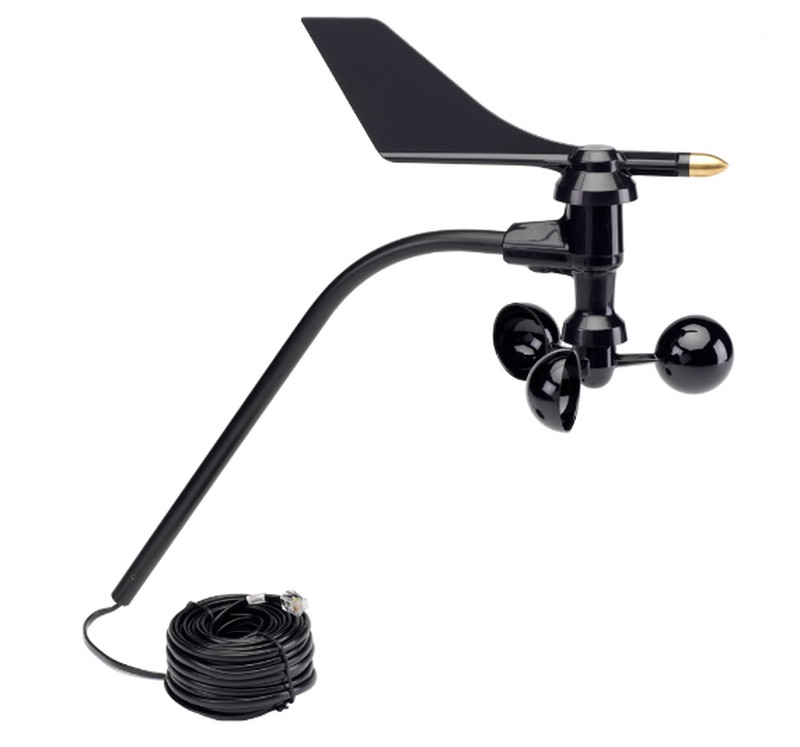
- Fixed anemometers associated with weather stations or other equipment:
They are the anemometers associated with the set of sensors or ISS of the automatic meteorological stations. They are installed permanently in a specific place and are used for real-time data recording and climatic characterization of the place where they are installed.
It is a more precise instrument and can also be installed independently (associated with its own datalogger), if you only want to monitor the wind. For example, on the highway, train tracks, ports, ships, etc ...
- Installation:
An anemometer must be officially installed at a height of 10m in a turret. As this installation is in many cases utopian, a base user should install it in the most open place possible in order to avoid obstacles and record the most realistic values possible.
In certain uses, such as agriculture, anemometers can be installed 2m above the ground or at a similar height of the crop in question.







Opinions of our clients
Receive our news